Status of Hunger in India
- Union Health Ministry has launched an initiative aimed at spreading awareness about nutrition and locally available nutritious food, fruits, and vegetables, a statement in April 2021.
- Vijnana Bharati (Vibha), ‘Global Indian Scientists and Technocrats’ (GIST) Forum, Vigyan Prasar, and Pravasi Bharatiya Academic and Scientific Sampark (PRABHASS) have come together to launch mission “Aahaar Kranti” with the motto of ‘Uttam Aahaar-Uttam Vichaar’ (Good Diet-Good Cognition). “Aahaar Kranti” movement is designed to address the peculiar problem being faced by India and the world — hunger and diseases in abundance.
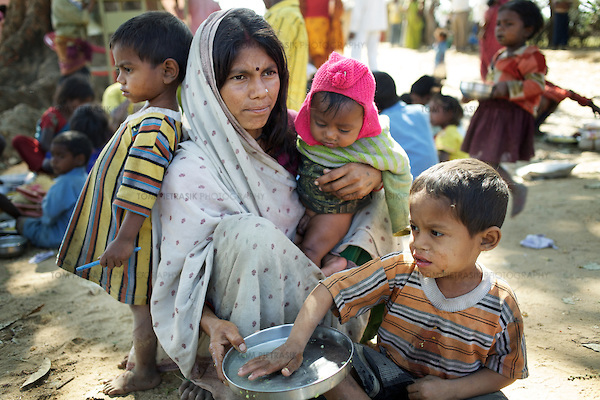
- The mission is launched because India ranked 94 among 107 nations in the Global Hunger Index 2020 (Jointly published by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe) and is in the ‘serious’ hunger category.
- The neighbouring Bangladesh (75th), Myanmar (78th) and Pakistan (88th) too are in the ‘serious’ category but ranked higher than India in this year’s hunger index. Nepal in 73rd and Sri Lanka in 64th position are in ‘moderate’ hunger category, the report showed.
- According to the report, 14 per cent of India’s population is undernourished. It also showed the country recorded a 37.4 per cent stunting rate among children under five and a wasting rate of 17.3 per cent. The under-five mortality rate stood at 3.7 per cent.
GHI is based on four indicators
- The proportion of undernourished in a population
- The proportion of children under the age of five suffering from wasting (less weight in proportion to their height)
- The proportion of children under five suffering from stunting (low height in proportion to their age)
- The mortality rate of children under five
Government Steps to Reduce Hunger:
- Eat Right India Movement : An outreach activity organised by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) for citizens to nudge them towards eating right.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan : Launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2018, it targets to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls).
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana : A centrally sponsored scheme executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is a maternity benefit programme being implemented in all districts of the country with effect from 1st January, 2017.
- Food Fortification : Food Fortification or Food Enrichment is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
- National Food Security Act, 2013 : The National Food Security Act, (NFSA) 2013 legally entitled up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Mission Indradhanush : It targets children under 2 years of age and pregnant women for immunization against 12 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (VPD).
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme : Launched on 2nd October, 1975, the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme offers a package of six services (Supplementary Nutrition, Pre-school non-formal education, Nutrition & health education, Immunization, Health check-up and Referral services) to children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013 : It provides for food and nutritional security in the human life cycle approach, by ensuring access to adequate quantities of quality food at affordable prices to people to live a life with dignity. Coverage includes 75% of the rural population and up to 50% of the urban population for receiving subsidized food grains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS). Under this act, 5 Kgs of foodgrains per person per month at Rs. 3/2/1 per Kg for rice/wheat/coarse grains.
Latest Blogs:
Status of Hunger in India